Businesses generate and collect vast amounts of location-based data—demographics, customer foot traffic, supply chain movements competitor positioning, weather, and more. Businesses can transform this raw data from multiple sources into actionable insights using advanced data processing services, driving smarter decisions, better business performance, and competitive advantage. Whether it’s optimizing store locations, improving delivery routes, or understanding market trends within a specific region, location intelligence has become a necessity. Let’s explore why every business, regardless of industry, needs it.
What is Location Intelligence and Why is it Important?
IBM defines location intelligence as “the method of gaining insights from geospatial data”.
Location-specific data is derived from GPS devices, mobile apps, IoT sensors, satellites, government databases, surveys, social media check-ins, and business transactions. Data processing for location intelligence involves collecting, cleaning, analyzing, and visualizing this geospatial data to derive actionable insights. These insights help recognize patterns, make predictions, and provide real-time understanding of location-specific questions.
From a business standpoint, location intelligence offers a powerful competitive edge through three key benefits:
- Deeper insights: By analyzing location data, companies can gain a deeper understanding of business processes, customer behavior, and operational outcomes. This drived more strategic decision-making.
- Real-time decisions: With continuously updated geospatial data, businesses can respond instantly to market changes, customer movements, and logistical challenges.
- Improved efficiency: Integrating location data with traditional business metrics provides a comprehensive operational view, eliminating silos and streamlining workflows.
According to a Boston Consulting Group (BCG) global survey commissioned by Google, covering more than 500 executives across different industries, several sectors depend on mapping and geospatial data to enhance business processes. Of the executives surveyed, 95% said that mapping and geospatial data are important in achieving desired business results, and 91% said that it will be even more essential in three to five years.
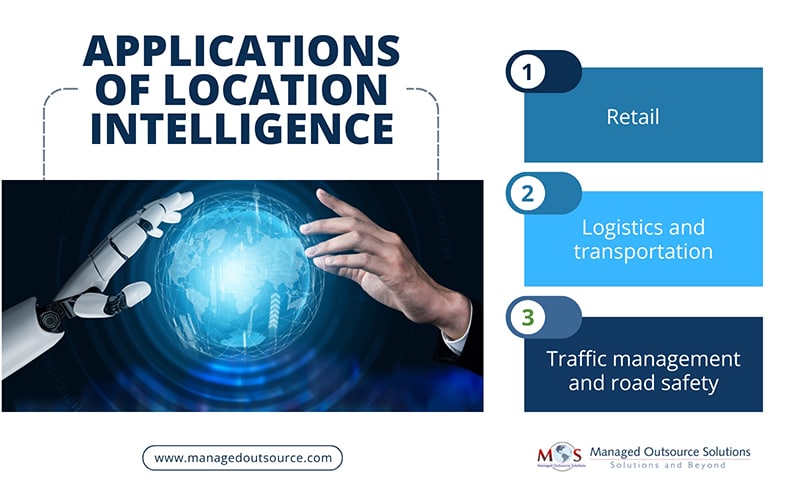
Applications of Location Intelligence
Retail: Factors like demographics, spending patterns, and income levels play a crucial role when choosing a business location. Location intelligence enables retailers to analyze these variables, identify high-potential areas, and segment customers into meaningful clusters for targeted marketing.
Beyond site selection, LI enhances the customer experience—with user consent, businesses can leverage real-time location data and external factors like traffic conditions to personalize interactions and optimize services. A common example is Google Maps, which suggests nearby places based on a user’s past visits, helping businesses connect with the right audience at the right time.
Logistics and transportation: In logistics and transportation, factors like route efficiency, delivery timelines, and traffic conditions are critical for smooth operations. Location intelligence helps businesses analyze these variables in real time, optimizing routes, reducing fuel costs, and improving delivery speed.
Location intelligence also improves fleet tracking and predictive analytics, allowing businesses to predict potential delays caused by weather, road conditions, or traffic congestion. For example, apps like Uber use location intelligence to determine the fastest routes and adjust pricing based on demand and traffic patterns, ensuring efficient transportation and improved customer satisfaction.
Traffic management and road safety: Road safety depends on factors like traffic flow, accident-prone zones, and weather conditions. Location intelligence helps identify high-risk areas by analyzing real-time data from GPS, traffic cameras, and historical accident reports, enabling authorities to implement targeted safety measures. It can also help prevent accidents by identifying hazardous road conditions. For example, navigation apps use location intelligence to alert drivers about potential hazards, road closures, and traffic slowdowns, making travel safer and more efficient.
Here are some examples of key industry-specific questions location intelligence can address:
- Retail and marketing – Where should I open my next store based on customer demographics and foot traffic?
- Logistics and supply chain – What’s the most efficient delivery route to reduce fuel costs and delays?
- Real estate and urban planning – How does proximity to schools, parks, or businesses affect property values?
- Finance and risk management – Where should banks open new branches based on demand and competition?
- E-commerce and delivery services – Which areas have the highest demand for same-day delivery?
How to Use Location Intelligence
- The first step is to define the problem and identify why location component is important to make a clear difference.
- The next step is to find a way to measure and access geolocation information.
- Once you have clean and accurate data, put it in the right format for training the algorithm. This is one of the essential steps in the process, as the quality of the model is only as good as the quality of the data used for its training.
- Make different prototypes of the model and test them against the real world.
- Keep testing until you have the best working model, making slight changes to inputs to check for performance and accuracy even in non-standard situations.
- Allow the model self-learn to potentially uncover other not so obvious connections within the data sets.
Ensuring Data Accuracy for Location Intelligence
Location intelligence is only as valuable as its accuracy. Inaccurate location data can undermine the effectiveness of any campaign that relies on it, leading to poor decision-making and missed opportunities. To ensure precision, businesses can partner with a BPO outsourcing company specializing in data entry, cleansing and processing services, and maintain accurate location data for reliable analysis and informed decision-making.
Eliminate errors and inconsistencies in your data with professional data cleansing services.