The way we generate content today is being revolutionized by technological advancements. Innovative technologies make it possible for content producers, marketers, and publishers to create multifaceted customer experiences. There are countless options that allow publishers to bring fresh creativity to the classics and companies to turn corporate upskilling into a compelling experience. But with all of the technical advancements, it’s easy to confuse different options available and associated terminologies. Publishers, authors, and content creators must grasp the differences between ePUB and eBook formats in the rapidly changing world of digital publishing. Although the terms are sometimes used synonymously, they refer to different ideas that have the potential to have a big influence on how well digital content performs. eBook conversion services play a crucial role in transforming content into various formats, including ePUB, enhaning accessibility and reach.
What is ePUB?
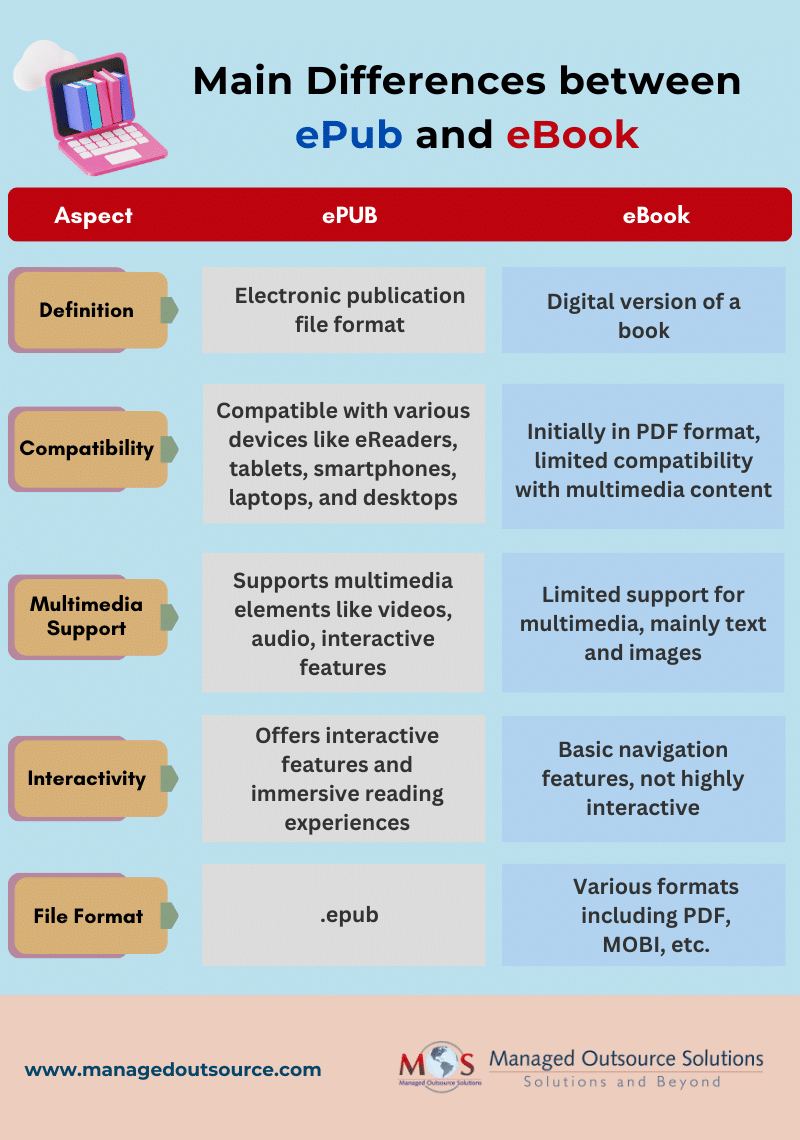
The International Digital Publishing Forum (IDPF) developed EPUB, an industry standard format that is digital native and meant to be seen on screen. It is currently overseen by the Word Wide Web Consortium (W3C). As it leverages current HTML standards, it is the most flexible and universally accessible format for digital content for everyone. The way the EPUB is presented is a lot like a webpage.
What is an eBook?
A digital book that can be read on a computer, tablet, or mobile device is known as an ebook or “electronic book.” An eBook can be created using non-editable text and graphic elements and is often available for download as a PDF and it is one of the most popular ebook formats. Originally developed by Adobe as a proprietary format, the PDF is a static document format that is now recognized by ISO. A copy of the print file can be viewed online with our webPDF. The ‘fixed layout’ ensures that all layout elements, such as columns, picture positioning, text boxes, images, special characters, and equations, are the same as in the print version. Page by page, the eBook in PDF format is displayed.
eBooks were first published as digital copies of print books. They were often released in PDF format, which allowed for links, text, and photos. The PDF format does, however, have some restrictions. They don’t support multimedia material, for example. Due to this, content producers, publishers, and marketers increasingly choose to release eBooks in the ePUB file format. Since ePUB is compatible with more devices than any other eBook format, it’s popularity is soaring. eBooks are now available for easy download on a variety of platforms, including tablets, smartphones, laptops, desktop computers, and eReaders. ePUB 3.3, the most recent version, offers even more flexibility by enabling authors to incorporate audio files, movies, and other interactive multimedia components.
Advantages of ePUB versus PDF eBooks
ePUB is preferred over PDF eBooks for a number of reasons:
-
- eBooks in ePUB format are more portable. ePUB extensions are kept in a zip file, in contrast to PDFs. As a result, ePUB files are lighter and don’t require the user to physically adjust their size. They reflow automatically in accordance with the device’s requirements. It is not necessary for users to manually zoom in and out. As a result, readability is better than ePUB.
- The ability to incorporate multimedia, including audio representation, video, quizzes, gamification, and other forms of interactive material, is yet another great benefit of ePUB eBooks. All eBooks are available to everyone, allowing users to read and consume content as they see fit.
- Language barriers are now being broken by ePUB eBooks because it is now simpler to produce them in multiple languages. Businesses can expand their market shares and attract new consumers by publishing in different languages.
The Future of ePUB and eBooks
In the coming years, ePUB and eBooks will be crucial in expanding business prospects and audience reach. For instance, ePUB eBooks hold much potential for use in higher education.
Educators are constantly seeking ways to increase the effectiveness of learning and broaden their scope. They can do so more easily if they make ePUB eBooks a central component of their efforts. With ePUB eBooks, educational institutions and teachers can create a more immersive, engaging, and dynamic learning environment and make learning accessible to all. These eBooks have a number of features that are not available in print or PDF textbooks. For example, educators and learners can underline significant passages in the book. Users can search for chapters much more quickly and write comments. Students can therefore participate in collaborative learning. Videos and animations can be used to clarify complex ideas. Students who struggle with reading can benefit from audio explanations to keep them up to date.
Want to create eBook?
Read our blog post:
Seven Steps to Create a Successful Ebook
While ePUB and eBooks are closely related concepts, understanding their differences is crucial for successful digital publishing. eBook conversion services bridge the gap between content creation and distribution by converting content into ePUB format and optimizing it for digital platforms. By leveraging these services, publishers can enhance their reach, accessibility, and reader engagement, paving the way for a dynamic and innovative publishing landscape.
Unlock the full potential of your digital content.
Ask for professional ePUB conversion or eBook conversion services.